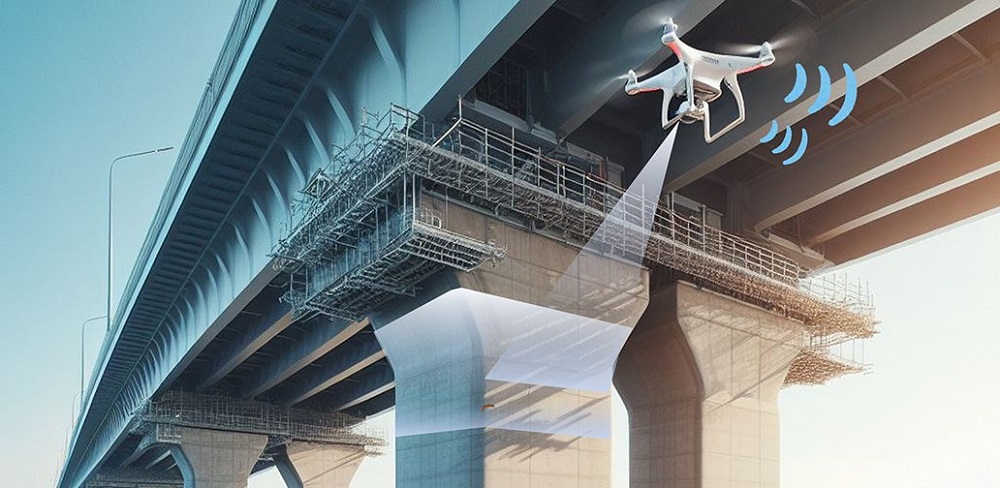

Identifying crumbling infrastructure is sometimes as difficult as rectifying it. Yet, this process has been made easier thanks to an innovative new material developed by Tohoku University researchers.
The material responds to mechanical stimuli by recording stress history through a luminescent effect called an afterglow. This information is stored for a long time, and by applying the material to the surfaces of structures, researchers can observe changes in the afterglow to determine the amount of stress the material has experienced.
"What makes our material truly innovative is that it operates without a power supply, complex equipment, or on-site observation and is easily combined with IoT technology," points out Tohoku University professor and corresponding author of the study, Chao-Nan Xu.
In Japan, aging infrastructure has become a significant problem, leading to an increased demand for new diagnostic technologies that prevent accidents and/or extend the life of structures.
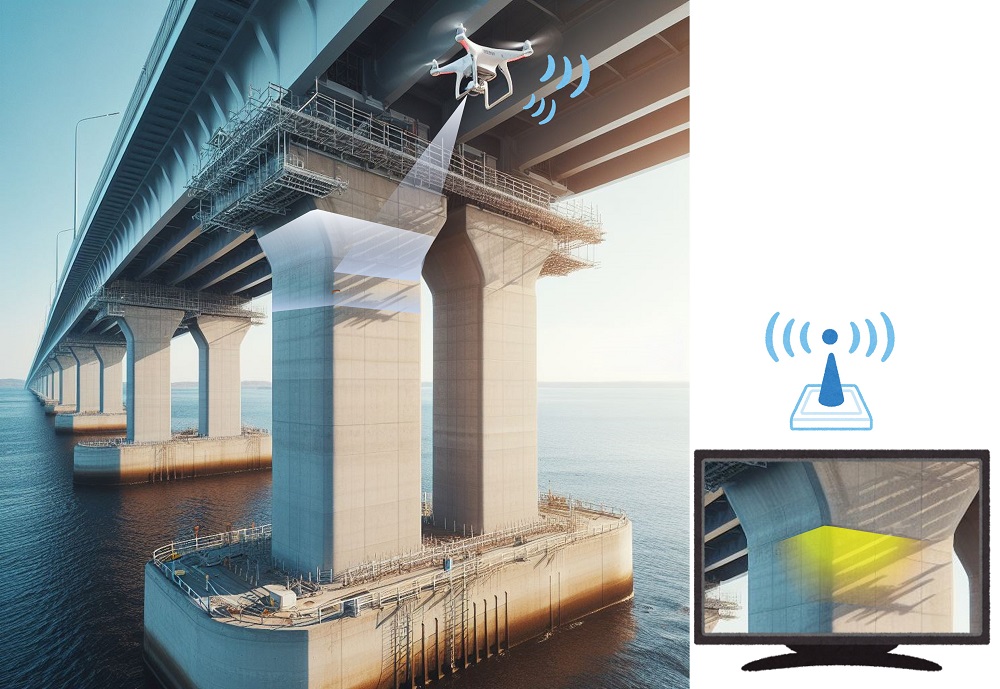

Structural Health Diagnosis combined with IoT technology. ©Tomoki Uchiyama, Chao-Nan Xu et al.
Mechanoluminescent materials exhibit luminescence when mechanically stimulated, and technologies such as crack detection and stress visualization have been developed by applying this material to the surface of structures. But the luminescence can only be observed at the moment of mechanical stimulation, and information about past mechanical stimuli cannot be retrieved.
Researchers have explored various materials capable of recording past mechanical loading histories. These materials typically combine stress-luminescent materials with photosensitive materials, creating a system where the material emits light in response to mechanical stress, and this light can be preserved and later analyzed to reconstruct the stress history. However, these materials face several challenges: complex layering structures, dark reactions, and long-term recording performance. Additionally, while certain fluorophores reveal past loading history when subjected to heat, the application has been limited to materials capable of withstanding high temperatures.
Xu and her colleagues discovered a simple and environmentally friendly method to record stress using Pr-doped Li0.12 Na0.88 NbO3 (LNNO). This LNNO had a mechanical recording functionality, meaning it could retrieve even past stress events.
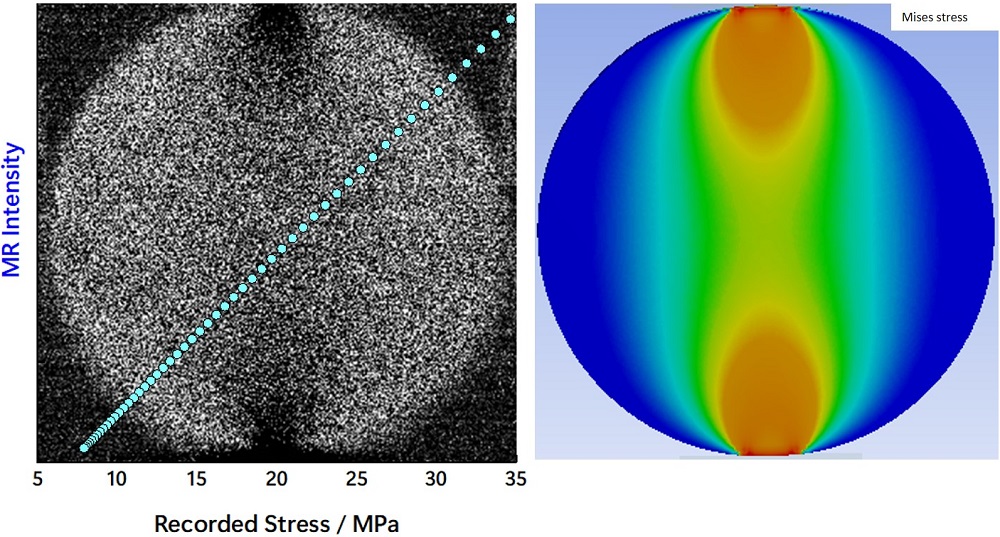
This study represents the stress recording (MR) function of multi-piezo mechanoluminescent material Li0.12Na0.88NbO3 through afterglow for the first time. Unlike traditional ML materials that solely enable real-time measurement of mechanical information, the novel MR capability is expected to be highly valuable for capturing the historical distribution of stress. ©Tomoki Uchiyama, Chao-Nan Xu et al.
To retrieve past stress information, LNNO is applied as a coating on the surface of an object and then irradiated with a flashlight. The afterglow produced by LNNO can be measured using cameras or light sensors. The study demonstrated that the afterglow image matches quantitatively with the results obtained through finite element method analysis. Additionally, the research confirmed that LNNO retains this stress information even after a period of five months.
"Our findings are expected to alleviate the shortage of manpower in structural diagnosis, and lower costs," adds Xu.
Also involved in the study was Tomoki Uchiyama, an assistant professor at Tohoku University, along with undergraduate students Taisei Atsumi and Koki Otonari. Yuki Fujio from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology and Xu-Guang Zheng from Saga University and Tohoku University.
Details of the findings were published in the journal Applied Physics Letters on April 25, 2024.